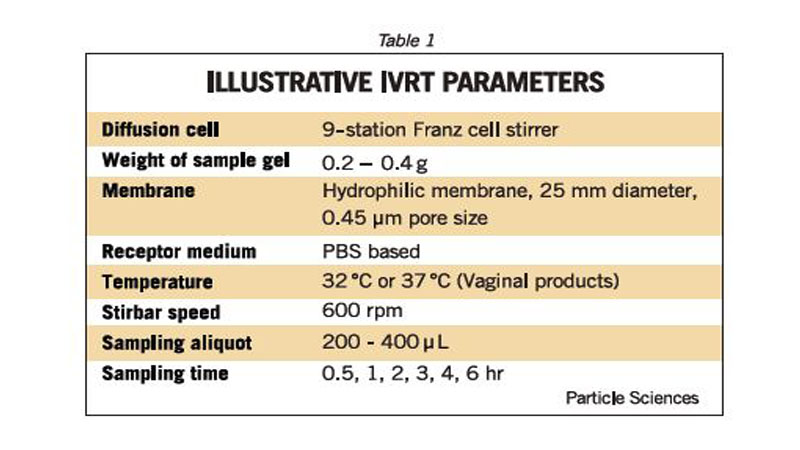
Multi Station Franz Diffusion Cell System
The measurement of drug release from a given dosage form is fundamental to drug product development.
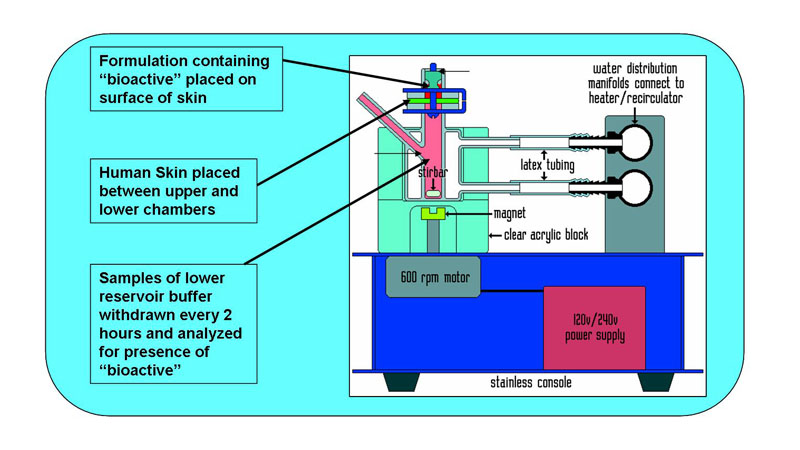
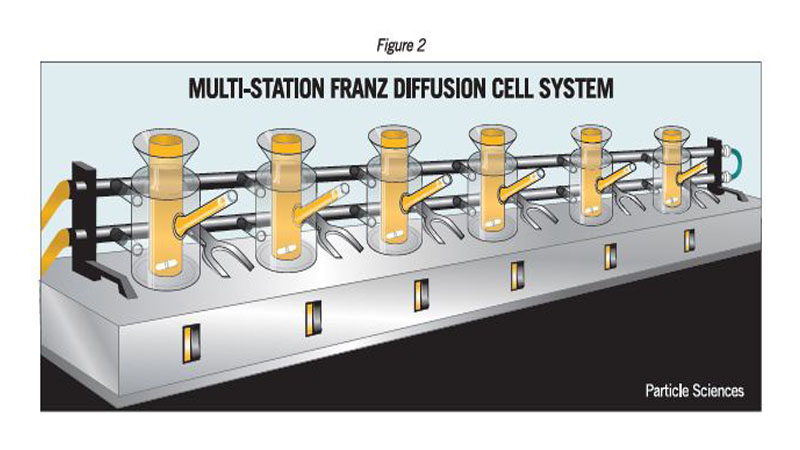
The most common IVRT method employs an open chamber design like the Franz diffusion cell system (Figures 1 and 2) and can be used with a synthetic membrane, a tissue construct, or biological sample, such as cadaver skin. The membrane separates the donor compartment containing the test product from the receptor compartment filled with collection medium. Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS) tends to the collection medium of first choice, though it may not always satisfy the requirements for a viable IVRT method. Diffusion of the drug from the semisolid product across the membrane is monitored by assay of sequentially collected samples of the receptor medium. At predetermined time points, an aliquot of medium is removed from the receptor compartment for drug content analysis, usually by HPLC. The receptor compartment is topped off with fresh medium after each sampling.